Training Rspamd Naive-Bayes
1. Collect samples
- Save spam emails into a folder, e.g.
spam/ - Save legitimate emails into a folder, e.g.
ham/
2. Move the data into the container
Assuming your folders are on the host system, copy them into the rspamd container:
docker cp spam/ rspamd:/tmp/spam
docker cp ham/ rspamd:/tmp/ham
3. Install the rspamd client inside the container
docker exec -it rspamd apk add rspamd-client
4. Check rspamd Statistics
docker exec -it rspamd rspamc -P tuxguard stat
Look for the line total learns: to see how many samples have been processed so far.
5. Train the model with your samples
Note, that you need a minimum of 200 ham samples to enable the bayes model.
docker exec -it rspamd rspamc -P tuxguard learn*spam /tmp/spam/*.eml
docker exec -it rspamd rspamc -P tuxguard learn*ham /tmp/ham/*.eml
6. Verify training
docker exec -it rspamd rspamc -P tuxguard stat
The total learns count should increase.
Example with downloaded spam messages
If you don’t yet have enough of your own spam samples, you can bootstrap training using a public dataset, e.g. https://untroubled.org/spam/:
Download a sample spam archive
cd /tmp
curl -o 2022.7z <https://untroubled.org/spam/2022.7z>
Extract the archive (Note you might need to install 7z: dnf install epel-release; dnf install p7zip)
7za x 2022.7z
Copy extracted messages into the container
docker cp 2022/ rspamd:/tmp/spam
Train on these samples
docker exec -it rspamd rspamc -P tuxguard learn_spam /tmp/spam/\*
After this, run rspamc stat again and confirm that the number of learned samples has gone up.
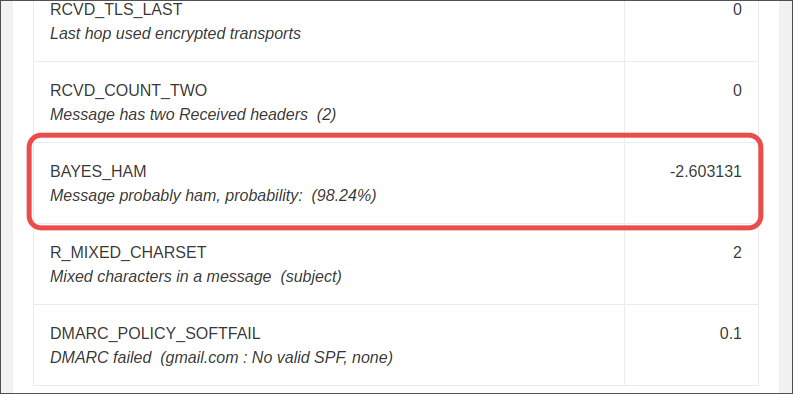
Afterward Rspamd will report the Bayes symbol in the log: